Advancements in technology are paving the way for improved patient care and healthcare delivery. However, with these advancements come significant challenges in data security. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is a critical regulation that those in the field of healthcare and in businesses that handle protected health information must adhere to.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into what HIPAA means to your facility or business, and provide an in-depth checklist for compliance.
Understanding HIPAA Compliance
What is HIPAA?
HIPAA, or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, was enacted in 1996. Its primary aim is to protect patient health information (PHI) from being disclosed without the patient’s consent or knowledge. This federal law mandates standards for healthcare providers, health plans, and healthcare clearinghouses to maintain the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of PHI.
The Importance of HIPAA Compliance
For businesses in the healthcare industry, HIPAA compliance is not just a legal requirement but a fundamental part of maintaining patient trust. Non-compliance can result in severe penalties and damage to an organization’s reputation. In 2023, a staggering 79.7% of data breaches in healthcare were attributed to hacking, a figure projected to rise even higher this year.
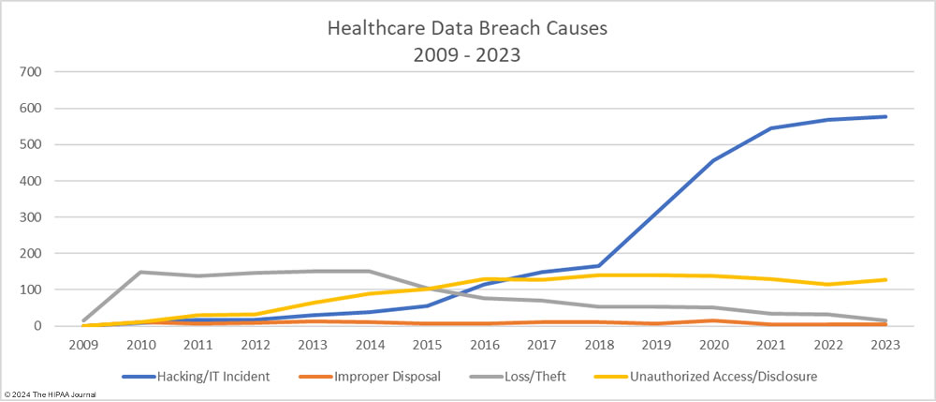
Scope of HIPAA Regulations
HIPAA regulations cover various aspects of healthcare, including electronic health records, billing, and patient communications. These regulations apply to healthcare providers, health plans, and business associates who handle PHI. Understanding the scope of HIPAA is crucial for ensuring comprehensive compliance across all levels of an organization.
HIPAA Compliance Checklist
Adhering to HIPAA regulations can often seem overwhelming due to the sheer breadth of requirements and the ever-changing landscape of data security threats. To simplify this process, we have compiled a detailed HIPAA compliance checklist. This checklist is designed to guide your organization through the fundamental steps needed to achieve and maintain HIPAA compliance, ensuring that patient information remains secure and that your facility or business is protected from potential breaches and penalties. Below, you’ll find the key components to focus on as you work towards comprehensive HIPAA compliance.
Administrative Safeguards
Administrative safeguards are policies and procedures designed to clearly show how your organization will comply with the act. These include the designation of a privacy officer responsible for developing and implementing privacy policies, conducting regular risk assessments, and providing ongoing training to staff about HIPAA regulations. Establishing comprehensive administrative safeguards ensures that everyone in the organization understands their role in protecting patient information and maintains a proactive approach to data security.
- Security Management Process – The first step in achieving HIPAA compliance is to establish a security management process. This involves conducting a thorough risk analysis to identify potential vulnerabilities within your organization. Once identified, implement appropriate security measures to mitigate these risks.
- Assigned Security Responsibility – Assigning security responsibility to a designated officer or team ensures that there is clear accountability for HIPAA compliance. This individual or group will oversee the development, implementation, and maintenance of HIPAA policies and procedures.
- Workforce Security – Workforce security is essential for preventing unauthorized access to PHI. Implement strict access controls and ensure that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive information. Regularly review and update access permissions as necessary.
Physical Safeguards
Physical safeguards are critical components of HIPAA compliance, focusing on the physical access to facilities and equipment that store PHI. These measures are designed to prevent unauthorized individuals from gaining physical access to PHI and ensure the overall security of the healthcare organization’s physical infrastructure.
- Facility Access Controls – Facility access controls involve implementing policies and procedures to limit physical access to facilities where PHI is stored. This includes secure areas such as server rooms and filing cabinets. Only authorized personnel should have access to these locations, and access logs should be maintained to monitor entry and exit.
- Workstation Use and Security – Workstation use policies help dictate the appropriate use of workstations and the security measures that must be in place to protect PHI. This can include having screensavers with automatic time-outs, ensuring workstations are not easily visible to the public, and educating staff on the proper handling and disposal of PHI.
- Device and Media Controls – Device and media controls pertain to the policies and procedures regarding the receipt, removal, and disposal of hardware and electronic media that contain PHI. This includes implementing measures for securely backing up data, the proper disposal of devices that are no longer in use, and maintaining an inventory of all devices that store PHI.
- Facility Access Controls – Controlling physical access to facilities that house PHI is as important as digital security measures. Implement access controls such as keycard systems, security cameras, and visitor logs to prevent unauthorized individuals from accessing sensitive areas.
- Workstation Use and Security – Ensure that workstations used to access PHI are secure. This includes positioning screens to prevent unauthorized viewing, using privacy filters, and implementing automatic screen lock features to protect information when the workstation is unattended.
- Device and Media Controls – Implementing device and media controls is crucial for securing PHI stored on portable devices and media. Establish policies for the use, disposal, and re-use of devices and media containing PHI to prevent unauthorized access or data breaches.

Technical Safeguards
By incorporating robust technical safeguards into your HIPAA compliance strategy, your organization can mitigate the risk of data breaches, cyberattacks, and unauthorized access to sensitive patient information. The following sections outline the key technical safeguards that must be put in place to ensure comprehensive ePHI protection.
- Access Control – Access control mechanisms are vital for ensuring that only authorized individuals can access PHI. Use unique user IDs, strong passwords, and multi-factor authentication to enhance security.
- Audit Controls – Maintaining audit controls allows organizations to monitor and record access to PHI. Regularly reviewing audit logs helps identify potential security incidents and ensures compliance with HIPAA regulations.
- Integrity Controls – Integrity controls ensure that PHI is not altered or destroyed in an unauthorized manner. Implement mechanisms such as encryption and digital signatures to protect the integrity of sensitive data.
Policies and Procedures
Establishing comprehensive policies and procedures is the backbone of effective HIPAA compliance. By developing, implementing, and regularly updating HIPAA policies and procedures, your organization can foster a culture of compliance and accountability. Here are some critical policies and procedures that should be incorporated into your HIPAA compliance program.
- Data Encryption – Encrypting PHI both at rest and in transit ensures that even if unauthorized access occurs, the information remains unreadable.
- Risk Analysis and Management – Conduct regular risk analyses to identify potential vulnerabilities and implement measures to mitigate these risks. A proactive approach to risk management helps maintain compliance and protects patient information.
- Incident Response Plan – An incident response plan outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a security breach. Having a well-defined plan ensures a swift and effective response, minimizing the impact of the breach and maintaining compliance.
Training and Awareness
Through comprehensive training programs and continuous awareness initiatives, organizations can empower their staff to recognize and respond to security risks, fostering a culture of vigilance and accountability.
- Employee Training on HIPAA Regulations – Regular training sessions on HIPAA regulations are essential for ensuring that all employees understand their responsibilities. Training should cover the basics of HIPAA, specific organizational policies, and procedures for handling PHI.
- Regular Security Awareness Programs – Implement ongoing security awareness programs to keep HIPAA compliance top-of-mind for employees. These programs should highlight the latest security threats and best practices for protecting sensitive information.
- Testing and Evaluation Processes – Regularly test and evaluate your HIPAA compliance measures to ensure they are effective. Conduct internal audits and engage third-party experts to assess your organization’s adherence to HIPAA regulations.
Maintaining Compliance
Achieving and maintaining HIPAA compliance is an ongoing process that requires constant vigilance and dedication. Here are some best practices necessary for maintaining robust HIPAA compliance on a continuous basis.
- Documentation and Record-Keeping Requirements – Proper documentation and record-keeping are essential for maintaining HIPAA compliance. Ensure that all policies, procedures, and training sessions are thoroughly documented and readily accessible for review.
- Role of Designated HIPAA Compliance Officers – Designate a HIPAA compliance officer to oversee all aspects of HIPAA compliance within your organization. This individual will be responsible for developing, implementing, and maintaining compliance measures.
- Addressing Changes in Regulations and Technology – HIPAA regulations and technology are constantly evolving. Stay informed about changes in regulations and advancements in technology to ensure your organization remains compliant. Regularly update your policies and procedures to reflect these changes.
Final Words
In a world where cybersecurity threats are on the rise, protecting sensitive patient information is essential. By following the action steps above, your organization can maintain HIPAA compliance, preserve patient trust, and avoid costly penalties. Be sure to stay informed about future trends in healthcare data security and continuously adapt your practices to ensure ongoing compliance.
About hubTGI
hubTGI is a Canadian-owned Managed Services provider that offers Print Services, Workflow Solutions, Managed IT, Cybersecurity Solutions, Cloud Services and VoIP to help their customers control costs, secure their data and make their people more productive.
For the latest industry trends and technology insights visit hubTGI’s Resources page.






